Photometry¶
HostPhot can calculate the photometry of the entire galaxy (global) or in a given circular aperture (local). For this, the code heavily relies on astropy and photutils. Note that the only surveys that need background subtraction are 2MASS, WISE and VISTA, which is performed by default.
Local Photometry¶
Local photometry can be obtained for the downloaded images. For this, a circular aperture is used (multiple apertures can be set), assuming a cosmology (H0=70 and Om0=0.3 by default; hence a redshift is needed):
import hostphot.local_photometry as lp
ap_radii = [3, 4] # aperture radii in units of kpc
results = lp.multi_band_phot(name, ra, dec, z,
survey=survey, ap_radii=ap_radii,
use_mask=True, correct_extinction=True,
save_plots=True)
results is a dictionary with the photometry (flux and magnitudes) of the filters used (the results are saved into a CSV file). Note that the coordinates are at the position of the object (SN2004eo). The cosmology can be changed with lp.choose_cosmology(). Setting use_mask=True tells HostPhot to used the masked images previously created (see Image Pre-processing) and setting save_plots=True provides output plots with the images and the apertures used, which are saved under the object’s directory.
Image with local aperture:
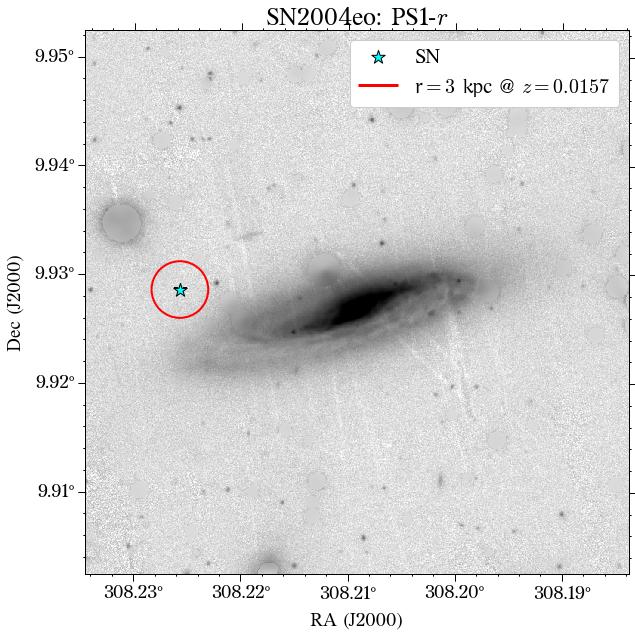
The green star marks the position of the SN and the red circle the aperture used.
Global Photometry¶
Global photometry relies on sep and uses Kron fluxes. It works in a relatively similar way to the local photometry:
import hostphot.global_photometry as gp
results = gp.multi_band_phot(name, host_ra, host_dec,
survey=survey, ra=ra, dec=dec,
use_mask=True, correct_extinction=True,
common_aperture=True, coadd_filters='riz',
save_plots=True)
Setting common_aperture=True tells HostPhot to used the same aperture for all the filters, obtained from the coadded image (coadd_filters='riz'; see Image Pre-processing) and setting optimize_kronrad=True provides a more “reliable” aperture than using the default parameters commonly used by SExtractor, as the aperture is increased until the change in flux is samller than a given percent (this can be changed with eps). The rest of the parameters are the same as before.
Image with global aperture:
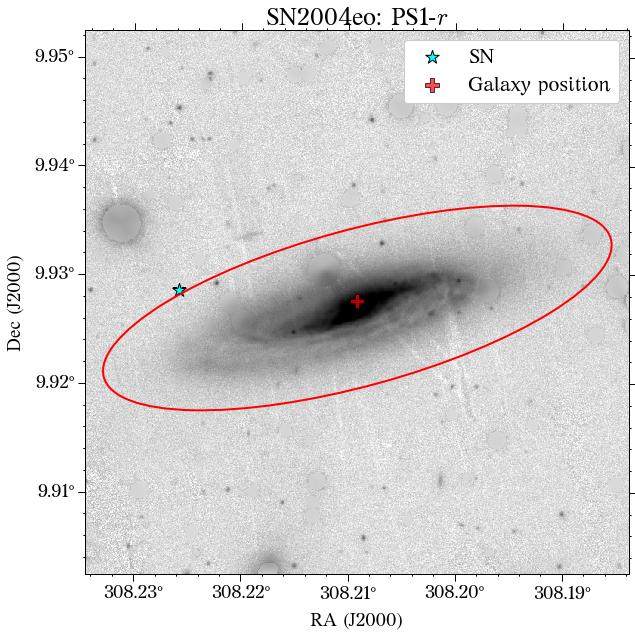
The parameters ra and dec are only used to plot the position of the SN. By default, HostPhot corrects for Milky Way extinction using the recalibrated dust maps
by Schlafly & Finkbeiner (2011) and the extinction law from Fitzpatrick (1999).